While ‘Work from home’ and hybrid work culture is slowly becoming a new normal for workers, network admins have to ensure that the remote worker has secured wireless and wired connectivity while they are working from their home. Some network admins would say why not have the remote workers VPN into the corporate network and we are all set but what about the VoIP phones and other Cisco features that network admin can leverage to monitor the devices. Although VPN to corporate network is an easy solution, resolving VPN issues while not having any access to the home router could be very difficult for the network admins.
Cisco’s OEAP (Office Extended Access Point) solution allows network admins to extend the secure, scalable and manageable Corporate WLAN across the internet to the remote workers. This allows the remote worker to securely connect back to the private network from their home without having to set up a VPN or other type of remote access. Remote users will be able to access to corporate resources, and “feel” as if they are connected to the wireless network at the corporate office. Also, this makes it very easy for the network admins to troubleshoot network problems as all the traffic will be controlled through WLC.
Why is OEAP better than VPN?
| Feature | OEAP | VPN |
| Connectivity to Corp Network | ✅ | ✅ |
| Split Tunneling | ✅ | ✅ |
| Easy Device Onboarding | ✅ | ❌ |
| RLAN support for wired Users | ✅ | ❌ |
| Voice device connectivity | ✅ | ❌ |
| VLAN splitting | ✅ | ❌ |
| Separate WLANs for home devices | ✅ | ❌ |
| Network admin monitoring | ✅ | ❌ |
| Complete visiblity to network for troubleshooting | ✅ | ❌ |
| Separate NAT network for non corporate client devices | ✅ | ❌ |
How does it work and is it easy deploy?
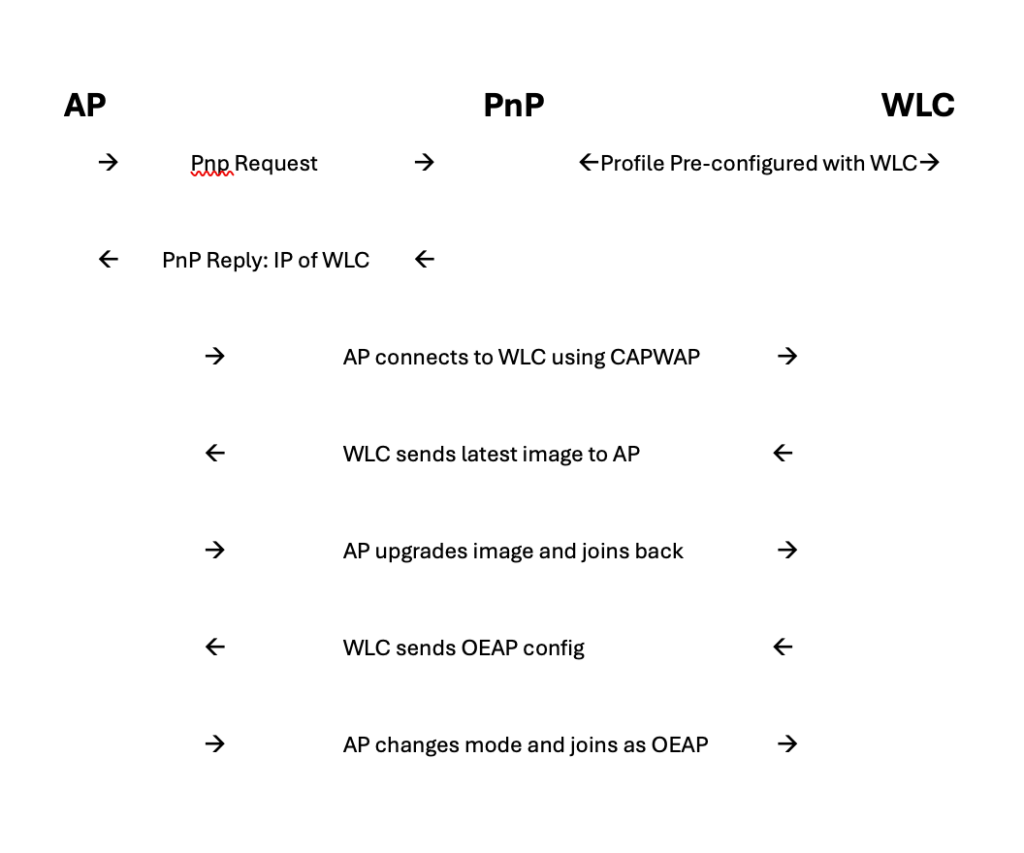
Network admins might think if OEAP is offering so many features it might come with a lot of pre-configuration work on the APs but that is not the case. Cisco PnP cloud and the Cisco 9800 WLC together make this experience a Zero Touch Deployment. Here’s how it works-
- Admins can use Cisco PnP (Plug and Play) cloud which will have controller profiles defined based on AP serial numbers.
- The controller profile has the information about the primary and secondary IP address of the corporate WLC. The admin can simply import the AP serial numbers using a CSV file and assign them a controller profile.
- AP sends CAPWAP request to the WLC IP and when the WLC sends a CAPWAP discovery response it downloads the AP image from the WLC and joins the WLC.
- WLC sends OEAP configuration to the AP and AP boots back and comes up in OEAP mode and will start broadcasting the WLANs defined in the WLC policy.
I will elaborate on OEAP configuration in next blog, stay tuned…
Related Blogs-
Cisco Wireless Features
Comprehensive Reads
Quick Reads